In the world of cryptocurrency, Blockchain technology has become the foundation of most cryptocurrency systems. However, a new technology is gradually attracting the attention of investors and industry experts, which is DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph). But do you know “What is DAG Blockchain?” and how is it different from traditional Blockchain models? Let’s explore it in detail in this article.
What is DAG Blockchain?
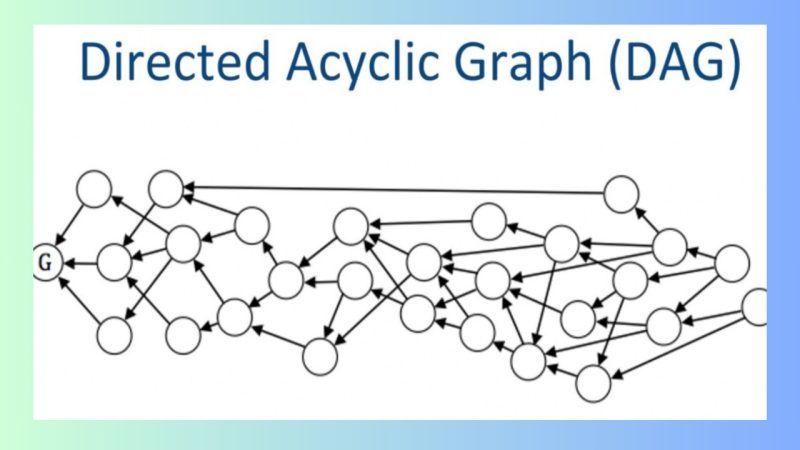
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a data structure used in various fields, especially in Blockchain technology. Unlike traditional Blockchain models, where data is organized into successive blocks, DAG Blockchain uses a directed graph to store transactions. Each vertex in this graph represents a transaction, and new transactions are validated through previous ones.
This means that in DAG, there are no blocks as in a conventional Blockchain system. Instead, transactions are directly connected, forming a graph with vertices and edges. This provides several notable advantages, including no limitations related to block times and the ability to process transactions simultaneously.

Structure and operating principles of DAG Blockchain
In a DAG system, each transaction is connected to previous ones, forming a network of linked transactions. When a new transaction is created, it refers to prior transactions, eliminating the need to wait for confirmation as in traditional Blockchain models. This significantly reduces waiting times and speeds up transaction processing.
A distinctive feature of DAG is the absence of the “block” concept, meaning it doesn’t face issues related to block time or network congestion like traditional Blockchain systems. Transactions can be confirmed simultaneously, allowing the system to handle a large volume of transactions without performance issues.
Advantages and disadvantages of DAG Blockchain
Advantages of DAG Blockchain
- Increased transaction speed: One of the standout advantages of DAG is its ability to process transactions quickly. Unlike traditional blockchain models, where transactions need to be confirmed in blocks, DAG allows transactions to be confirmed simultaneously. Each new transaction references and validates older transactions, creating a seamless transaction network without the limitations of block creation times. This dramatically boosts transaction speeds, especially in networks with high transaction volumes.
- No transaction fees or very low fees: In a DAG system, users don’t need to pay transaction fees or only pay very small amounts. This is a significant improvement over traditional blockchains, where transaction fees can rise depending on network congestion. In DAG, since there are no blocks to mine, miners are not required, and there are no mining fees. This is particularly beneficial for small-value transactions, such as those in IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
- Scalability: DAG doesn’t face the scalability issues that traditional blockchains do, where transaction volumes are limited by block creation times and the computational power of miners. In DAG, scalability is improved through simultaneous transaction processing. This means that the more participants there are in the network, the stronger the network becomes, and the better it can handle transactions.
- Energy efficiency: Unlike blockchains that use energy-consuming algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) such as Bitcoin or Proof of Stake (PoS) like Ethereum 2.0, DAG doesn’t require miners to validate transactions. This significantly reduces energy consumption, making DAG an environmentally-friendly option compared to traditional blockchains.
- Decentralized Network: The DAG model helps avoid the concentration of power in miners or stakers. Instead, every participant in the network can contribute to transaction validation, maintaining decentralization and ensuring fairness and efficiency throughout the ecosystem.
Disadvantages of DAG Blockchain
- Power and control issues: While DAG enhances decentralization, there are still some issues related to the concentration of power within the system. Some DAG protocols may have centralized aspects in their operation, especially in the early stages of network development. Developers and operators may retain a larger share of control compared to other network participants, which could lead to fairness and transparency concerns in the network’s operation.
- Vulnerability to spam attacks: With transaction fees close to zero, DAG systems are susceptible to spam attacks. Malicious actors can generate a large number of fake transactions, congesting the network and reducing system performance. While there may be mechanisms to mitigate this issue, the risk of attack remains, especially when a DAG system is still in its early stages of development and hasn’t been widely tested.
- Difficulty in implementing complex features like smart contracts: Compared to traditional blockchains like Ethereum, DAG is not an ideal solution for deploying complex smart contracts. Due to the structure of DAG, developing decentralized apps (dApps) with complex features may present technical challenges. Apps requiring sophisticated calculations and logic might face difficulties when deployed on a DAG platform.
- Requires further testing and development: Despite its many benefits, DAG technology is still in its early developmental stages. Platforms using DAG, such as IOTA and Nano, are not yet widely popular and still need time for testing and optimization. This could cause concerns for investors and users regarding the stability and reliability of DAG-based projects.
- Challenges in controlling and maintaining scalability: Some DAG projects might face challenges when it comes to scaling. While DAG networks can handle a large volume of transactions, maintaining security and stability as the network grows could be difficult, especially in environments with millions of users.
DAG Blockchain in the cryptocurrency market
DAG Blockchain is not just a theoretical model for how transactions work; it has already been successfully implemented in several prominent cryptocurrency projects. Notable examples include Nano, IOTA, and U2U Chain, which showcase how DAG operates in the cryptocurrency world.
Nano: Enhancing transaction speed and reducing fees
Nano is a project that uses DAG in its Block-Lattice system, where each account has its own separate blockchain. This is in stark contrast to traditional blockchain models like Bitcoin, where all transactions are stored in consecutive blocks. With Block-Lattice, each transaction is recorded on an independent chain, with no interaction with other transactions outside the participants involved.
Nano’s benefits include:
- No transaction fees: Transactions are fast and don’t suffer from network congestion.
- High scalability: Since each account has its own blockchain, Nano can process transactions without running into congestion issues, making the network stronger and more flexible.
- Energy-efficient: Nano doesn’t use energy-consuming algorithms like PoW or PoS, making it a very energy-efficient solution with nearly zero transaction costs.
IOTA: Expanding applications for the Internet of Things (IoT)
IOTA is another project using DAG, but unlike Nano’s Block-Lattice, IOTA implements a system called Tangle. Tangle is a form of DAG where each new transaction validates two previous transactions. This means when users perform a transaction, they not only get their transaction confirmed but also help validate others’ transactions.
The advantages of IOTA include:
- Scalability: IOTA can easily scale by processing millions of transactions simultaneously without congestion.
- Low or no transaction fees: Transactions in IOTA require no fees, making it suitable for IoT applications where a large number of transactions take place.
- Ideal for IoT: IOTA offers an ideal solution for connecting and transacting between smart devices in a decentralized network.

U2U Chain: A breakthrough in DePIN and modular Blockchain
U2U Chain is a new blockchain project that uses DAG to solve common issues in traditional blockchain systems, such as transaction speed and fees. With the development of DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network), U2U Chain leverages DAG to optimize its network, especially in areas like IoT, wireless networks, and decentralized storage.
U2U Chain aims to provide a modular blockchain platform, allowing applications and dApps to run on independent subnets while ensuring security and compatibility with the main network. DAG helps U2U Chain by:
- Accelerating transaction speeds: Transactions are processed quickly and simultaneously, reducing confirmation times.
- Lower transaction fees: By using DAG, U2U Chain offers low-cost transactions, particularly in DePIN applications.
- Flexible scalability: With its modular blockchain network, U2U Chain can scale without sacrificing performance, thanks to DAG’s transaction processing capabilities.
U2U Chain is developing a robust ecosystem with over 80 dApps, more than 1 million users, and over 100,000 daily active users. The DAG technology in U2U Chain contributes to creating an efficient payment and transaction system, helping blockchain enter real-world applications such as IoT and wireless networks.
In conclusion, this article has helped explain in detail what “DAG Blockchain” is. It can be said that DAG Blockchain is a promising technology offering significant advantages in speed, cost, and scalability. However, it still faces challenges such as security and decentralization. With the rapid development of technology, DAG could become an important part of the future of the cryptocurrency market.
Don’t forget to follow the latest articles on Digicash Blog to stay updated with information and insights about blockchain technology and the investment finance market every day!